HOLISTIC WELLNESS FOR KIDS
Babies and children usually respond well to homeopathic treatment, as their natural vitality kicks the immune system into action quickly. Homeopathy can help them with a wide range of problems such as: coughs, colds and fevers; teething, nappy rash, colic, eczema, asthma, sleep and digestive problems, as well as recurrent infections. Children are normally very happy to take the remedies as they don’t have an unpleasant taste and dissolve easily on the tongue. Homeopathy can also be extremely helpful in supporting children and young people emotionally, with issues such as anxiety (including exam nerves!) and shyness, aggression, temper tantrums and ADHD. It can also make a difference to children on the autistic spectrum.
It is also very effective for older children and teenagers for hormonal imbalance; skin and menstrual problems; recurrent tonsillitis and glandular fever. Homeopathy can fill an important gap in the treatment of viral infections as conventional treatment in this area is limited.

Our homoeopathy wing give special attention in treating following conditions in kids:
- Allergy and asthma
- After effects of tb and pneumonia
- Adenoids with mouth breathing
- Tonsillitis with throat pain
- Recurrent fever and febrile fits
- Nocturnal eneuresis (bed wetting)
- Poor immunity and underweight
- Warts and molluscum
- Eczema ,snuffles(noseblock), colic, teething disorders in infants
- Hyperactivity disorder(adhd)
- Cerebral palsy
- Developmental coordination disorders
- Autistic spectrum disorders

MOLLUSCUM CONTAGIOSUM :
Molluscum contagisoum is a form of warts caused by a virus that infects the skin. Very common in children, it causes multiple small, fleshy bumps to appear on the trunk, arms, face, and other areas. While not dangerous, molluscum lesions can be itchy, inflamed, and unsightly. People can get molluscum by sharing towels and clothing. Wrestlers and gymnasts may get it from touching infected mats. Skin-to-skin contact also spreads the virus and can last for months, or even years but via scratching, the virus can spread and inoculate new sites and keep the condition going. Physicians seldom offer treatment but when parents insist on removing the unsightly bumps, conventional treatments can involve removing the lesions surgically or with a laser, or applying a topical medication. The approaches typically do not work very well because they do not address the root cause of the problems, which is that the body is harboring a virus.
This virus easily spreads from person to person.
Most people get about 10 to 20 bumps on their skin. If a person has a weakened immune system, many bumps often appear.
Molluscum Contagiosum is contagious.
INFANTILE COLIC :
Colic is commonly described as a behavioral syndrome in neonates and infants that is characterized by excessive, paroxysmal crying. Colic is most likely to occur in the evenings, and it occurs without any identifiable cause.
Signs and Symptoms
In the setting of colic, a detailed history should be obtained regarding the following:
- Timing of crying: Crying by infants with or without colic is mostly observed during evening hours and peaks at the age of 6 weeks
- Amount of crying: The amount of crying is not related to an infant’s sex; the mother’s parity; or the parents’ socioeconomic status, education, or ages
- Characteristics of crying: Compared with regular crying, colicky crying is more turbulent or dysphonic and has a higher pitch
- Family’s daily routine
- possible other causes of excessive crying (eg, having hair in the eye, strangulated hernia, otitis, sepsis); colic remains a diagnosis of exclusion
Signs and Symptoms
General management principles include the following:
- Rule out common causes of crying
- Recommend that the parents not exhaust themselves, and encourage them to consider leaving their baby with other caretakers for short respites
- Consistent follow-up and a sympathetic physician are the cornerstones of management
- Various benign but unproven treatment modalities are available, including the following:
- Maternal low-allergen diet (i.e., low in dairy, soy, egg, peanut, wheat, and shellfish) may offer relief from excessive crying in some infants.
- Lactobacillus reutter
- Oral hypertonic glucose
- Behavioral management
- Nutritional supplements and other complementary medicines
Dietary changes may include the following:
- Elimination of cow’s milk protein in cases of suspected intolerance of the protein
- In infants with suspected cow’s milk allergy (CMA), a protein hydrolysate formula is indicated
- Soy-based formulas are not recommended, because many infants who are allergic to cow’s milk protein may also become intolerant of soy protein
INFANTILE SNUFFLE OR CATARAH
Catarrh is usually the symptom of a cold, but it can occur with other illnesses such as measles and flu. Your child may experience a runny nose, nasal congestion, snuffling, coughing, and even vomiting of mucus and food in an effort to clear the chest, In itself, catarrh is not serious, but it can cause a baby distress and make things difficult for you. Babies always breathe through their nostrils and only use their mouth if their nostrils are congested. Problems in feeding can arise and sleeping patterns can be disturbed for a while after the congestion has cleared.
General Management
- Keep your child propped up with extra pillows at night to avoid mucus running down the throat.
- As with asthma, it is important that the air is not too dry. Keep central heating low or off in the bedroom at night and try using a humidifier.
- Dairy products can lead to an over-production of mucus. Children under five do need fat and calcium in their diets, so make sure they get satisfactory substitutes.

ATOPIC ECZEMA :
Eczema and dermatitis are terms for a group of skin conditions that cause the skin to become inflamed or irritated. Learn about the causes, symptoms, treatment, and prevention of these common skin conditions.
Types
- Atopic dermatitis
- Contact dermatitis
- Dyshidrotic eczema
- Neurodermatitis
- Nummular dermatitis
- Stasis dermatitis
Triggers: What can cause eczema to flare?
Trigger: Anything that aggravates your child’s skin can either:
- Make eczema appear on the skin
- Worsen existing eczema

3 key facts about eczema triggers
Many things can trigger eczema — including dry air, sweat, and stress. A trigger that causes one child’s eczema to flare may not cause another child’s eczema to flare.
As a child grows older, eczema triggers can change.
How you can help your child
When a child has eczema, the child’s skin is extremely sensitive. The more sensitive the skin, the more susceptible it is to triggers. While finding triggers is important, you’ll see the best results when you follow these steps:
- Follow an eczema friendly 5 elements skin care plan
- Use eczema medicines and therapies as directed
- Manage your child’s triggers
When eczema is under control, a child can sleep peacefully
Is it possible to control eczema?
Yes, it is possible to control eczema. And, controlling eczema has benefits.
Controlling eczema can:
- Decrease flares
- Improve your child’s health and quality of life
- Reduce the amount of medicine needed — and the need for medicine

1st step: Understand eczema
Before learning how to control eczema, it’s helpful to learn a bit about eczema. This can help you understand what your child is experiencing. It can also help you care for your child’s eczema.
Basic facts about eczema
- Eczema causes inflammation in the skin.
- The skin becomes intensely itchy.
- Scratching tends to worsen the eczema, but it can be difficult to stop scratching because the skin is so itchy.
- Eczema is not contagious, but the dry, itchy, and inflamed skin may cause people to think it is.
- This common skin condition often begins before age 5.
Skin care: Does it help treat eczema

Baths and moisturizers play an important role in treating eczema. By bathing and moisturizing your child’s skin as your dermatologist recommends, you can:
- Ease your child’s discomfort
- Decrease eczema flares
- Improve your child’s response to treatment
- Reduce the need for medicine
BRONCHIAL ASTHMA :
How asthma is classified
To classify your asthma severity, your doctor considers your answers to questions about symptoms (such as how often you have asthma attacks and how bad they are), along with the results of your physical exam and diagnostic tests.
Determining your asthma severity helps your doctor choose the best treatment. Asthma severity often changes over time, requiring treatment adjustments.
Asthma is classified into four general categories:
Asthma classification
Signs and symptoms
Mild intermittent
Mild symptoms up to two days a week and up to two nights a month
Mild persistent
Symptoms more than twice a week, but no more than once in a single day
Moderate persistent
Symptoms once a day and more than one night a week
Severe persistent
Symptoms throughout the day on most days and frequently at night
Avoid your triggers
Taking steps to reduce your exposure asthma triggers is a key part of asthma control, including:
- Use your air conditioner. Air conditioning reduces the amount of airborne pollen from trees, grasses and weeds that finds its way indoors. Air conditioning also lowers indoor humidity and can reduce your exposure to dust mites. If you don't have air conditioning, try to keep your windows closed during pollen season.
- Decontaminate your decor. Minimize dust that may worsen nighttime symptoms by replacing certain items in your bedroom. For example, encase pillows, mattresses and box springs in dustproof covers. Remove carpeting and install hardwood or linoleum flooring. Use washable curtains and blinds.
- Maintain optimal humidity. If you live in a damp climate, talk to your doctor about using a dehumidifier.
- Prevent mold spores. Clean damp areas in the bath, kitchen and around the house to keep mold spores from developing. Get rid of moldy leaves or damp firewood in the yard.
- Reduce pet dander. If you're allergic to dander, avoid pets with fur or feathers. Having pets regularly bathed or groomed also may reduce the amount of dander in your surroundings.
- Clean regularly. Clean your home at least once a week. If you're likely to stir up dust, wear a mask or have someone else do the cleaning.
- Cover your nose and mouth if it's cold out. If your asthma is worsened by cold or dry air, wearing a face mask can help.
Stay healthy
Taking care of yourself can help keep your symptoms under control, including:
- Get regular exercise. Having asthma doesn't mean you have to be less active. Treatment can prevent asthma attacks and control symptoms during activity.
- Regular exercise can strengthen your heart and lungs, which helps relieve asthma symptoms. If you exercise in cold temperatures, wear a face mask to warm the air you breathe.
- Maintain a healthy weight. Being overweight can worsen asthma symptoms, and it puts you at higher risk of other health problems.
- Control heartburn and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). It's possible that the acid reflux that causes heartburn may damage lung airways and worsen asthma symptoms. If you have frequent or constant heartburn, talk to your doctor about treatment options. You may need treatment for GERD before your asthma symptoms improve.
- Breathing exercises. These exercises may reduce the amount of medication you need to keep your asthma symptoms under control.
measure the extent of possible side effects. Alternative asthma treatments include:
Our Approach :
Constitutional treatment is recommended for asthma. Where the child has been given a lot of conventional medicine your homeopath will have to antidote the side effects of them and make a platform for our medicines to act.
ADHD
- A behavior disorder in which the essential features are signs of developmentally inappropriate inattention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity.
- A behavior disorder originating in childhood in which the essential features are signs of developmentally inappropriate inattention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity. Although most individuals have symptoms of both inattention and hyperactivity-impulsivity, one or the other pattern may be predominant. The disorder is more frequent in males than females. Onset is in childhood. Symptoms often attenuate during late adolescence although a minority experience the full complement of symptoms into mid-adulthood.
- A disorder characterized by a marked pattern of inattention and/or hyperactivity-impulsivity that is inconsistent with developmental level and clearly interferes with functioning in at least two settings (e.g. At home and at school). At least some of the symptoms must be present before the age of 7 years.
- Is it hard for your child to sit still? does your child act without thinking first? does your child start but not finish things? if so, your child may have attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (adhd). Nearly everyone shows some of these behaviors at times, but adhd lasts more than 6 months and causes problems in school, at home and in social situations. Adhd is more common in boys than girls. The main features of adhd are
- inattention
- hyperactivity
- impulsivity
No one knows exactly what causes adhd. It sometimes runs in families, so genetics may be a factor. There may also be environmental factors.a complete evaluation by a trained professional is the only way to know for sure if your child has adhd. Structure at home and at school is important. Parent training may also help.
AUTISM SPECTRUM DISORDER :
- A disorder beginning in childhood. It is marked by the presence of markedly abnormal or impaired development in social interaction and communication and a markedly restricted repertoire of activity and interest. Manifestations of the disorder vary greatly depending on the developmental level and chronological age of the individual. (dsm-iv)
- A disorder characterized by marked impairments in social interaction and communication accompanied by a pattern of repetitive, stereotyped behaviors and activities. Developmental delays in social interaction and language surface prior to age 3 years.
- Autism is a disorder that is usually diagnosed in early childhood. The main signs and symptoms of autism involve communication, social interactions and repetitive behaviors. Children with autism might have problems talking with you, or they might not look you in the eye when you talk to them. They may spend a lot of time putting things in order before they can pay attention, or they may say the same sentence again and again to calm themselves down. They often seem to be in their "own world."because people with autism can have very different features or symptoms, health care providers think of autism as a "spectrum" disorder. asperger syndrome is a milder version of the disorder.the cause of autism is not known. Autism lasts throughout a person's lifetime. There is no cure, but treatment can help. Treatments include behavior and communication therapies and medicines to control symptoms. Starting treatment as early as possible is important. nih: national institute of child health and human development
- Disorder beginning in childhood marked by the presence of markedly abnormal or impaired development in social interaction and communication and a markedly restricted repertoire of activity and interest; manifestations of the disorder vary greatly depending on the developmental level and chronological age of the individual.
- Type of autism characterized by very early detection (< 30 months), social coldness, grossly impaired communication, and bizarre motor responses.
DEVELOPMENTAL CORDINATION DOSORDER :
A disorder characterized by an impairment in the development of an individual's motor coordination skills; this impairment in motor development is not due to a medical condition.
Marked impairments in the development of motor coordination such that the impairment interferes with activities of daily living.
MALNUTRITION :
Malnutrition refers to deficiencies, excesses, or imbalances in a person’s intake of energy and/or nutrients. The term malnutrition addresses 3 broad groups of conditions: undernutrition, which includes wasting (low weight-for-height), stunting (low height-for-age) and underweight (low weight-for-age); micronutrient-related malnutrition, which includes micronutrient deficiencies (a lack of important vitamins and minerals) or micronutrient excess; and overweight, obesity and diet-related noncommunicable diseases (such as heart disease, stroke, diabetes and some cancers).
TONSILLITIS :
What Are Tonsils?
The tonsils' job is to help fight germs that come in through our mouth or nose before they cause infections in the rest of the body. Usually, tonsils do their job well. But sometimes bacteria or viruses get into the tonsils and infect them. When this happens, you have tonsillitis.
ADENOIDS :
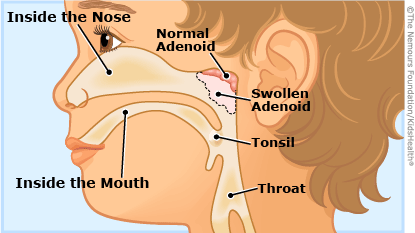
What Are Adenoids?
The adenoids (say: AD-eh-noyds) are a patch of tissue that sit in the back of the nasal cavity. Like tonsils, adenoids help keep your body healthy by trapping harmful bacteriaand viruses that you breathe in or swallow.
Adenoids do important work as infection fighters for babies and little kids. But they become less important as a kid gets older and the body develops other ways to fight germs. Adenoids usually shrink after about age 5, and by the teenage years they often practically disappear.
What Are Enlarged Adenoids?
Because adenoids trap germs that enter the body, adenoid tissue sometimes temporarily swells (gets puffier) as it tries to fight off an infection. The swelling sometimes gets better, but sometimes adenoids can get infected
Swollen or infected adenoids can make it tough to breathe and cause these problems:
- a very stuffy nose, so a kid can breathe only through his or her mouth
- snoring and trouble getting a good night's sleep
- swollen glands in the neck
- ear problems
Tell a parent if you have any of these problems, so he or she can take you to the doctor.
What Will the Doctor Do?
At the doctor's office, the doctor will ask you how things feel in your ears, nose, and throat, and then take a look at these parts. Your doctor will also feel your neck near your jaw.
To check the size of your adenoids, your doctor might ask you to get an X-ray or look in your nose with a tiny telescope
Homoeopathy for Adenoids:
There are very effective medicines to treat Adenoids which can show marked changes within 3 months and may be continued depends on the patient condition.
